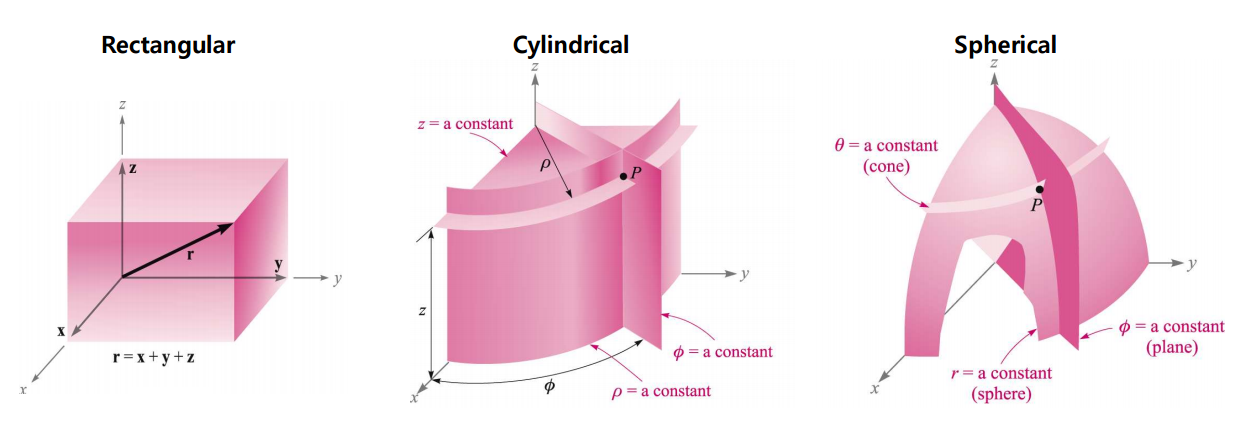
Coordinate System Rectangular Coordinate System 가장 흔하게 사용하는 좌표계로 ( x , y , z )로 표현된다. Cylindrical Coordinate System ( ρ , φ , z )로 표현된다. ρ : z축으로부터 점까지의 거리 φ : xy평면상에서 x축으로부터의 각도 z :높이(z좌표) Spherical Coordinate System ( r , θ , φ )로 표현된다. r : 원접으로부터 점까지의 거리 θ : z축으로부터의 각도 φ : xy평면상에서 x축으로부터의 각도 // Cylindrcal에서와 동일하다 좌표 표현 위치가 다르다 각 Coordinate System에서의 표현 동일한 위치의 점이라도 좌표계에 따라 위와 같이 다르게 표현될 수 있다.